| ENG RUS | Timus Online Judge |
Quarterfinal, Rybinsk, October 16 2003
Contest is over
H. River BasinTime limit: 1.0 second Memory limit: 64 MB 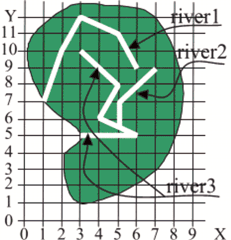 You are given a map of rivers of some continent. Every river is shown as a broken line, which begins with a river head and ends either at the point where the river flows into another one, or on the river mouth. The vertexes of the broken line are the turning points of the river-bed, or the points of tributary flow. We will consider the river basin as a convex polygon of minimum area that contains the river and all its tributaries. Remark. According to the definition of river basin the same territory may belong to the basins of different rivers. Sample. A continent with three rivers is shown. The coordinates of the rivers and areas of the basins are given in the table.
Your task is to calculate the maximum among all river basin areas. InputThe first line contains the number of the rivers N. The rest of the input contains N blocks describing the rivers. Each block i consists of:
Limitations. 0 < N <= 10, ∑ki <= 1000, -1000 <= xj, yj <= 1000. Clarifications.
Outputcontains one number – the area of the largest basin calculated with two digit precision. Samples
Problem Author: © Sergey G. Volchenkov, 2003(volchenkov@yandex.ru); Vladimir N. Pinaev, 2003(vpinaev@mail.ru; http://www.pic200x.chat.ru); Michael Y. Kopachev, 2003 (mkopachev@krista.ru). Problem Source: 2003-2004 ACM Central Region of Russia Quarterfinal Programming Contest, Rybinsk, October 15-16, 2003 |
