| ENG RUS | Timus Online Judge |
Ural Regional School Programming Contest 2010
Contest is over
H. Hamming CodeTime limit: 1.0 second Memory limit: 64 MB Let us consider four disks intersecting as in the figure. Each of the three shapes formed by the intersection
of three disks will be called a petal.
Write zero or one on each of the disks. Then write on each petal the remainder in the division by two of the sum
of integers on the disks that contain this petal. For example, if there were the integers 0, 1, 0, and 1 written
on the disks, then the integers written on the petals will be 0, 1, and 0 (the disks and petals are given in the
order shown in the figure).
This scheme is called a Hamming code. It has an interesting property: if you enemy changes secretely any
of the seven integers, you can determine uniquely which integer has been changed. Solve this problem and you will
know how this can be done.
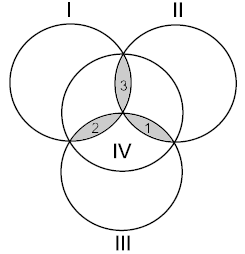 InputThe only line contains seven integers separated with a space, each of them being zero or one. The first four
integers are those written on the disks in the order shown in the figure. The following three integers are those
written on the petals in the order shown in the figure
OutputOutput one line containing seven integers separated with a space. The integers must form a Hamming code. The set
of integers may differ from the input set by one integer at most. It is guaranteed that either the input set is
a Hamming code or a Hamming code can be obtained from it by changing exactly one integer. Samples
Problem Author: Sofia Tekhazheva, prepared by Olga Soboleva Problem Source: Ural Regional School Programming Contest 2010 |
